Get ready for a better way to lose weight and keep it off at St. Vital Fit Body Boot Camp. Our workout classes in Winnipeg, MB, are designed to burn twice the calories and maximize fat burning results in only 30 minutes per day. Led by certified fitness coaches committed to helping you achieve your fitness goals, you won’t find a boot camp workout in Winnipeg that’s as transformative as what you’ll get at St. Vital Fit Body Boot Camp.
Reaching your weight loss goals is simple and easy when you join the Fit Body Boot Camp community, follow your custom nutrition program, and experience our Afterburn formulated workout classes. It’s time to start your fitness journey with the last workout program you’ll ever need so you can lose weight for the last time. Come in for the St. Vital Fit Body Boot Camp workout experience today!
It doesn’t matter if you’re an experienced gym goer or haven’t touched cardio or a weight in years, our boot camp workouts are formulated to work for everyone. We welcome all fitness levels to our Fit Body Boot Camp community where everyone is welcome and supported.


Burn fat and hit your goals in as little as 30 minutes with our Afterburn workouts that’ll have you burning calories even after you’re done.

Every fitness coach is an experienced certified personal trainer dedicated to motivating you and helping you lose weight for the last time.

Enjoy the amazing community of like-minded individuals motivated to help you lose weight for the last time.
We welcome all fitness levels to experience the St. Vital Fit Body Boot Camp workout in Winnipeg, MB. Join our transformative workout classes designed to help you lose weight for the last time with friendly certified coaches and a positive community to support and motivate you every step of the way.
We developed our signature workout formula, Afterburn, by combining two research-backed training methods for the most effective and sustainable weight loss we’ve ever encountered: High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Active Rest Training. They work together to decrease body fat, increase strength and endurance, increase athletic performance, and improve your overall health.
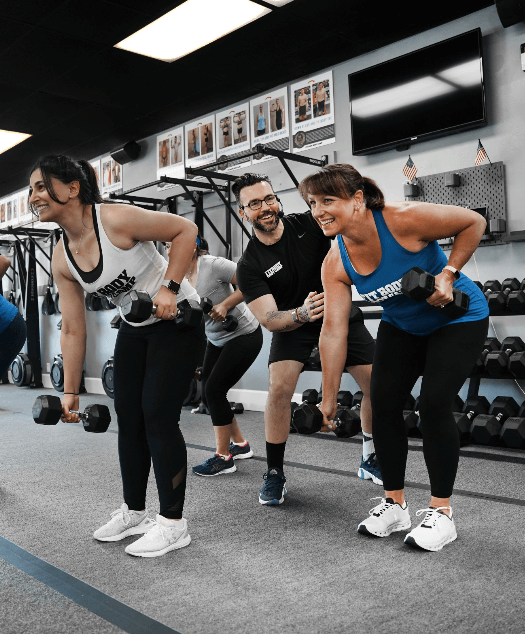
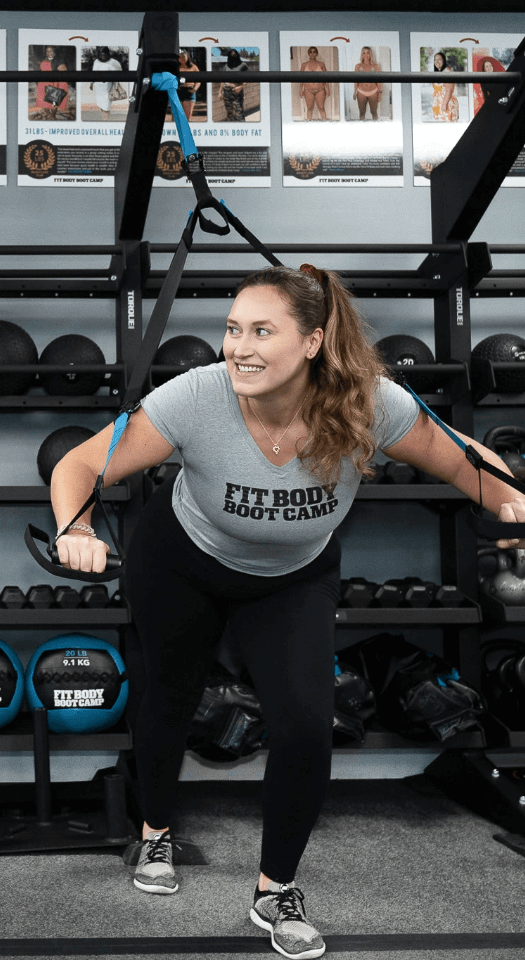


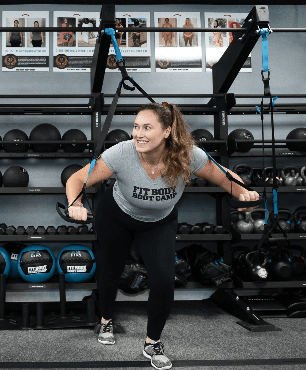
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) uses short bursts of activity to spike the metabolism and keep it running at an accelerated rate for up to 36 hours after the workout. That means the body burns extra calories even during sleep! During a HIIT workout, you’ll push your body to the limits of exhaustion, broken up by small periods of recovery. The key characteristics of High-Intensity Interval Training are maximal effort, duration, and short rest periods.
As an added bonus, this keeps every boot camp workout dynamic and engaging the whole way through. Those short 30 minutes will fly by even faster than you think because your mind and body are constantly stimulated by something new. Our experienced fitness coaches are always innovating and finding new ways to keep you motivated and plugged in.
HIIT is ideal for weight loss because it focuses on charging up the metabolism and increasing lean muscle. Since lean muscle burns slightly more calories at rest, that added muscle helps the body transform into a fat-torching furnace! And with a higher metabolism, the body burns more fat and enjoys higher energy levels throughout the day.
Active Rest Training fills in the gaps between exercises with exercises like jogging and active stretching that target different muscles. This keeps the heart rate going at 30% to 60% of the maximum heart rate while still giving the muscles time to rest and recover.
Studies show that Active Rest Training during workouts results in faster post-workout recovery. This provides minimal downtime and allows you to get back to your busy schedule. It also enables you to leap into your day full of energy and come back to boot camp the next day, ready to go!
Most importantly, Active Rest Training burns more calories in the same amount of time. This is because Active Rest keeps challenging the body and keeps the heart rate high throughout the whole boot camp workout.
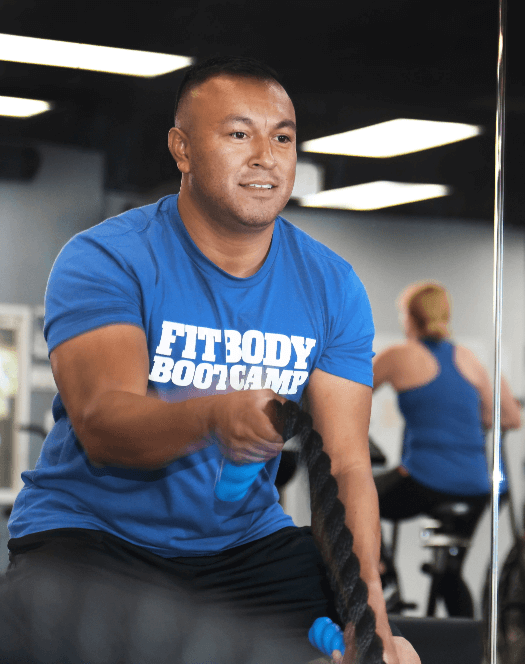
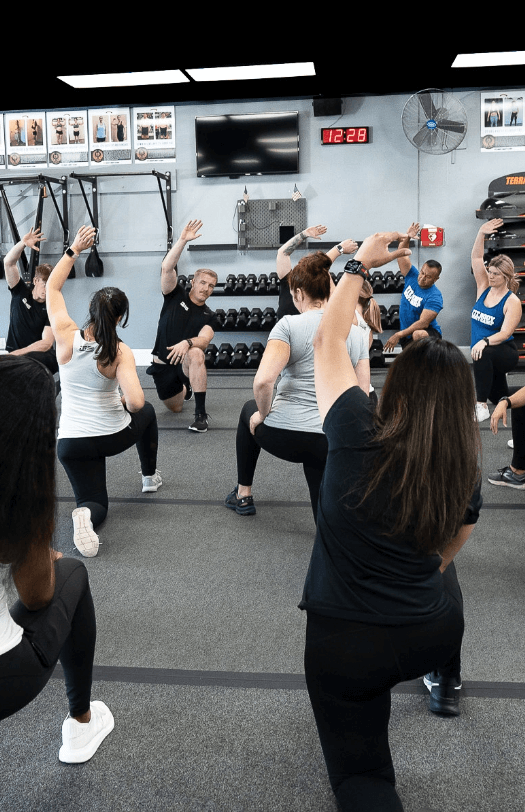

Our Afterburn formula, which combines HIIT and Active Rest Training, works for people of all fitness levels. We count on the expertise of our certified personal trainers, or as we call them here at Fit Body Boot Camp, fitness coaches. They check your form every step of the way to make sure you’re getting the maximum benefit from each exercise. They are also able even to modify exercises for you if you come in with a prior injury, making our boot camp workouts accessible for everyone!
Our goal is to make sure you’re safe, happy, and making progress with every second of every boot camp workout!
Have you had an injury in the past that affects your mobility or strength? Or are you concerned about injuries in general while working out?
Rest assured, we’ve thought of everything! If you have an existing injury, our friendly fitness coaches can easily modify any boot camp workout to make sure you still get the calorie burn and weight loss results you’re looking for. Our goal is to make fitness accessible and affordable for everyone. The last thing we want is for you to miss out on this awesome experience that goes way beyond just the workout. We want nothing to stand in your way to fitness, health, and being part of a supportive community.
At Fit Body Body Boot Camp, all of our workouts are programmed to be “Low Risk, High Reward.” There are plenty of high-risk exercises that athletes, bodybuilders, and weight lifters are willing to use in their training that simply aren’t necessary for weight loss. Because your goal is to lose fat and tone your muscles, we keep the exercises simple and safe so you can workout with confidence and peace of mind!
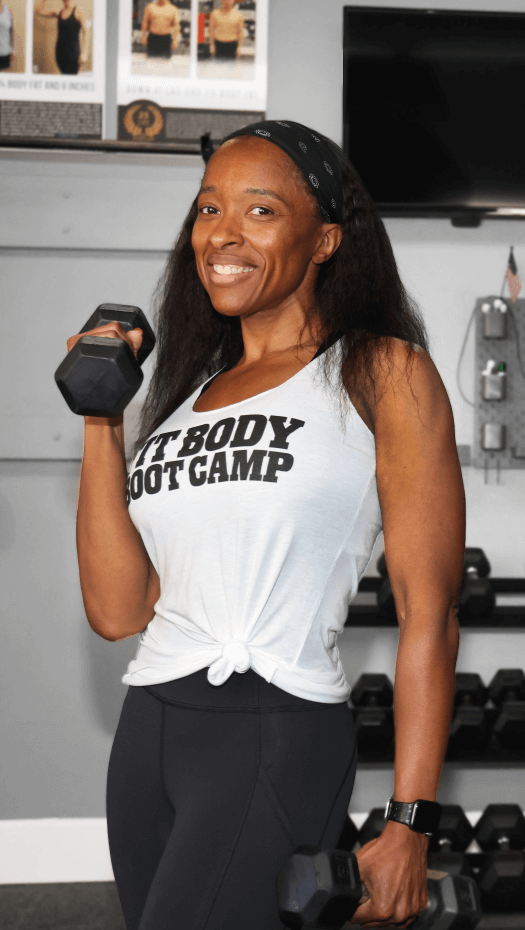
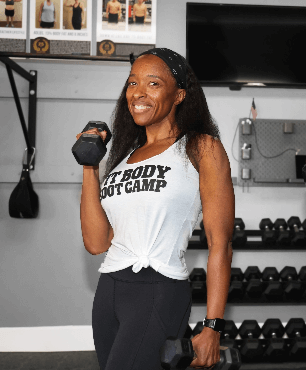

"Since my joining, my physical, mental and emotional health have improved. My recovery from having my third son was so much smoother than after my first two, which I attribute largely to Fit Body. My strength came back more quickly and for the first time, I had zero signs of postpartum depression. Wherever you are at in your fitness journey, I highly recommend giving MV Fit Body Boot Camp a try!"
Kimberly Ziaei | Mission Viejo, California
Mission Viejo, California

“If you are looking for an awesome, inclusive, fun, place to work out THIS IS IT! Fit Body is a fantastic place, the coaches are knowledgeable, fun and they push you and motivate you, no matter your fitness level you’ll feel challenged in every class. The classes are always different so you’ll never ever get bored.”
Maria Espinoza | Berkley, Michigan
Berkley, California

“Berkley Fit Body is AWESOME. When the boot camp style gym I previously went to closed, I was devastated and never thought another gym would compare. Not only does Berkley Fit Body meet the expectations set by my previous gym, it significantly exceeds them and provides me things I never knew I needed!”
Amber Chinoski | Berkley, Michigan
Berkley, California

"At my heaviest point and most unhealthiest, I decided to give this gym a try after a recommendation. I am SO glad I did! We are all a family and support each other 110%. No judging. I've learned how to eat healthy, have gotten incredibly strong, lost over 55 pounds, and am happy to stay in the best shape of my adult life.”
Kathy Llewellyn | Whitesboro, Texas
Whitesboro, Texas

“I was really hesitant when I signed up 2 months ago. I did not think I would enjoy the workouts and honestly had no clue if it would make a difference in my life. I was COMPLETELY wrong. Thanks to Fit Body, my body is slowly changing for the better and my confidence levels are growing. I honestly couldn't think of a better place/environment to help better your body and mind!”
Maegan Hess | Fern Creek, Louisville
Fern Creek, Louisville

“I am approaching my 2 years there at Fern Creek Fit Body. I have a BAD knee and thought I would try the place. I LOVE THIS PLACE. This place is for all people at all different levels of what each individual can do in a work out. I have lost some weight and I have built my confidence. Most of all I have a new extended family. Not only the staff but other members are always welcoming, helpful and encouraging.”
Dana Ballinger | Fern Creek, Louisville
Fern Creek, Louisville

“When I first started in November of last year, I had high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and I was pre-diabetic. I constantly felt tired, suffered from headaches almost everyday, and absolutely hated doing anything active because my back and my joints always hurt. Now, at almost 40, my energy level is better than it was in my 20s, my blood pressure is in the normal range and I’m no longer pre-diabetic. I recommend Fit Body to anyone and everyone who’s looking to make a positive change in their lives!!”
Penelope Melko | Sioux Falls, South Dakota
Sioux Falls, South Dakota
Let’s be real: 1-on-1 personal training is simply too expensive for most people to stick with long-term. Yet, if you want to see real progress and do it in a safe way, the best results will come from the personal care and attention that only a true fitness coach can provide. So, what’s the solution?
Our boot camp workouts have a solution already built in! In our small sessions, we typically have 20-30 attendees with 2 or more fitness coaches present. This allows you to split the cost of 1-on-1 training for dramatic savings — without sacrificing any of the same attention and care you need to reach your health and fitness goals.
You’ll get access to much more than that. You will also be plugged in from day one into our supportive and welcoming community of like-minded individuals. It is in these communities that you will find the support and motivation you need, even by just getting to know each other’s own fitness journey. There is much to learn from your peers, and they want to get to know you! Even outside of your boot camp workouts, you’re only one click, one text, or one call away from getting the motivation and tips you need to stay on track with your fitness journey.
Fit Body Boot Camp is a fitness franchise dedicated to transformation. 30 minutes per session is all it takes to help you reach your weight loss goals.
Fill out the form below to connect with your local Fit Body about how you can get started.
Fill out the form below to connect with your local Fit Body about how you can get started.